
Consequently, it is better to go directly to the equity side of the balance sheet. There, we will find Total stockholder’s equity, which is, as the name says, all that is in stockholder possession, including common stockholders and preferred stockholders. Earnings, debt, and assets are the building blocks of any public company’s financial statements. For the purpose of disclosure, companies break these three elements into more refined figures for investors to examine. Investors can calculate valuation ratios from these to make it easier to compare companies.
Mục Lục
Increase Assets and Reduce Liabilities
- Book value refers to a firm’s net asset value (NAV) or its total assets minus its total liabilities.
- A price-to-book ratio under 1.0 typically indicates an undervalued stock, although some value investors may set different thresholds such as less than 3.0.
- For instance, consider a company’s brand value, which is built through a series of marketing campaigns.
- But an important point to understand is that these investors view this simply as a sign that the company is potentially undervalued, not that the fundamentals of the company are necessarily strong.
- Like a person securing a car loan by using their house as collateral, a company might use valuable assets to secure loans when it is struggling financially.
For asset-heavy industries, BVPS might provide a reasonable estimate of value. However, for sectors like technology and pharmaceuticals, where intellectual property and ongoing research and development are crucial, BVPS can be misleading.
Why is BVPS important for value investors?
The stock is currently trading at 100 USD, with a market-to-book ratio of 1.3, meaning that it can still have space to increase its value per share up to the 2019 price-to-book ratio. The most significant benefit of our price-to-book ratio calculator is that you can quickly add information and promptly get the historical values for analysis. Furthermore, you can use all of our cool financial calculators to improve your investments’ risk-reward profile.
How to Interpret BVPS?
In contrast, video game companies, fashion designers, or trading firms may have little or no book value because they are only as good as the people who work there. Book value is not very useful in the latter case, but for companies with solid assets, it’s often the No.1 figure for investors. Preferred stock is usually excluded from the calculation because preferred stockholders have a higher claim on assets in case of liquidation. By repurchasing 1,000,000 common shares from the company’s shareholders, the BVPS increased from $3.00 to $4.50. An investor can apply BVPS to a stock by analyzing the company’s balance sheet. Specifically, an investor will need total asset value, cost of acquiring an asset, and accumulated depreciation of corporate assets which helps provide the most accurate BVPS figure.
Online Investments
Book value per share (BVPS) tells investors the book value of a firm on a per-share basis. Investors use BVPS to gauge whether a stock price is undervalued by comparing it to the firm’s market value per share. Book value refers to a firm’s net asset value (NAV) or its total assets minus its total liabilities. Since public companies are owned by shareholders, this is also known as the total shareholders’ equity.
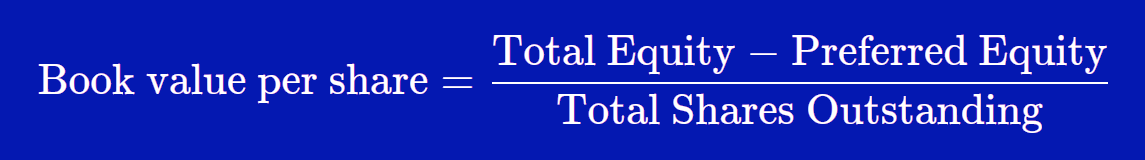
As a company’s potential profitability, or its expected growth rate, increases, the corresponding market value per share will also increase. A company can use a portion of its earnings to buy assets that would increase common equity along with BVPS. Or, it could use its earnings to reduce liabilities, which would also increase its common equity and BVPS. If a company’s share price falls below its BVPS, a corporate raider could make a risk-free profit by buying the company and liquidating it. If book value is negative, where a company’s liabilities exceed its assets, this is known as a balance sheet insolvency.
Book value per share is just one of the methods for comparison in valuing of a company. Enterprise value, or firm value, market value, market capitalization, and other methods may be used in different circumstances or compared to one another for contrast. For example, enterprise value would look at the market value of the company’s equity plus its debt, whereas book value per share only looks at the equity on the balance sheet. Conceptually, book value per share is similar to net worth, meaning it is assets minus debt, and may be looked at as though what would occur if operations were to cease. One must consider that the balance sheet may not reflect with certain accuracy, what would actually occur if a company did sell all of their assets. For instance, consider a company’s brand value, which is built through a series of marketing campaigns.
Knowing what book value per share is, how to calculate it, and how it differs from other calculations, can add yet another tool to an investor’s tool chest. Alternatively, another method to increase the BVPS is via share repurchases (i.e. buybacks) from existing shareholders. If relevant, the value of preferred equity claims should also be subtracted from the numerator, the book value of equity. Therefore, the book value per share (BVPS) is a company’s net asset value expressed on a per-share basis.
Critics of book value are quick to point out that finding genuine book value plays has become difficult in the heavily-analyzed U.S. stock market. Oddly enough, this has been a constant refrain heard since the 1950s, yet value investors continue to find book value plays. Failing bankruptcy, other investors would ideally see that the book value was worth more than the stock and also buy in, pushing the price up to match the book value.
U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) require marketing costs to be expensed immediately, reducing the book value per share. However, if advertising efforts enhance the image of a company’s products, the company can charge premium prices and electronic filing create brand value. Market demand may increase the stock price, which results in a large divergence between the market and book values per share. However, the market value per share—a forward-looking metric—accounts for a company’s future earning power.

Xin chào! Tôi là Luna Nguyễn người làm nội dung trên website: tracuudisc.com . Mọi góp ý của các bạn đều là động lực giúp chúng tôi hoàn thiện hơn vậy nên đừng ngại ngùng hãy comment suy nghĩ của các bạn khi trải nghiệm trên website tracuudisc.com nhé!
