
Significant differences between the book value per share and the market value per share arise due to the ways in which accounting principles classify certain transactions. If XYZ can generate higher profits and use those profits to buy more assets or reduce liabilities, the firm’s common equity increases. If, for example, the company generates $500,000 in earnings and uses $200,000 of the profits to buy assets, common equity increases along with BVPS. On the other hand, if XYZ uses $300,000 of the earnings to reduce liabilities, common equity also increases. It may not include intangible assets such as patents, intellectual property, brand value, and goodwill. It also may not fully account for workers’ skills, human capital, and future profits and growth.
Mục Lục
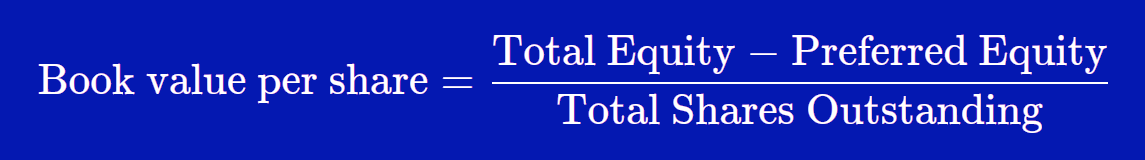
In theory, a low price-to-book-value ratio means you have a cushion against poor performance. Outdated equipment may still add to book value, whereas appreciation in property may not be included. If you are going to invest based on book value, you have to find out the real state of those assets. That said, looking deeper into book value will give you a better understanding of the company.
Is BVPS relevant for all types of companies?
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master’s in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem. Generally, the book value per share is used by investors (especially value investors) to determine whether a share is fairly valued.
Total annual return is considered by a number of analysts to be a better, more accurate gauge of a mutual fund’s performance, but the NAV is still used as a handy interim evaluation tool. A company’s stock is considered undervalued when BVPS is higher than a company’s market value or current stock price. If the BVPS increases, the stock is perceived as more valuable, and the price should increase. It is worth mentioning that the asset value recorded in the balance sheet is discounted by its depreciation period by period; thus, we should expect a decreasing equity value over time. That can happen; however, in successful companies, when the return on assets is high, constant, and stable, the depreciation effect is offset by the cash retained from the company.
The difference between a company’s total assets and total liabilities is its net asset value, or the value remaining for equity shareholders. Because book value per share only considers the book value, it fails to incorporate other intangible factors that may increase the market value of a company’s shares, even upon liquidation. For instance, banks or high-tech software companies often have very little tangible assets relative to their intellectual property and human capital (labor force). These intangibles would not always be factored in to a book value calculation. While BVPS considers the residual equity per-share for a company’s stock, net asset value, or NAV, is a per-share value calculated for a mutual fund or an exchange-traded fund, or ETF. For any of these investments, the NAV is calculated by dividing the total value of all the fund’s securities by the total number of outstanding fund shares.
Online Investments
- Finally, we will see how to calculate the price-to-book value ratio and apply it to a real example.
- You will need the number of shares outstanding obtained from the income statement.
- That said, looking deeper into book value will give you a better understanding of the company.
- Book value per share (BVPS) tells investors the book value of a firm on a per-share basis.
- A P/B ratio of 1.0 indicates that the market price of a share of stock is exactly equal to its book value.
- In the example from a moment ago, a company has $1,000,000 in equity and 1,000,000 shares outstanding.
When we mentioned that book value represents assets’ economic value if we pay all financial claims, we did not talk about non-physical assets. This means that each share of the company would be worth $8 if the company got liquidated. Now, let’s say that you’re considering investing in either Company A or Company B. Given that Company B has a higher book value per share, you might find it tempting to invest in that company. However, you would need to do some more research before making a final decision.
To calculate book value per share, simply divide a company’s total common equity by the number of shares outstanding. For example, if a company has total common equity of $1,000,000 and 1,000,000 shares outstanding, then its book value per share would be $1. Rather than buying more of its own stock, a company can use profits to accumulate additional assets or reduce its current liabilities. For example, a company can use profits to either purchase more company assets, pay off debts, or both. These methods would increase the common equity available to shareholders, and hence, raise the BVPS. If a company’s BVPS is higher than its market value per share (the current stock price), the stock may be considered undervalued.
In Particular, we can review if JPM stock became an exciting opportunity after the stock market crash. It provides services in the area of investment banking, commercial banking, and treasury services, among others. However, during the stock market crash of March 2020, the stock price declined by around 40%. In that sense, the 13 strategies to speed up collections price-to-book ratio compares the book value vs. the market value, showing us the market’s appreciation towards a company. We can say that if the market-to-book ratio is high, the market has huge expectations for the business’s future. Meanwhile, when such a ratio is low, it expresses investors’ disbelief regarding the company.
We designed our fantastic price-to-book ratio calculator to help you calculate both per-share values. You just have to click on the Price to tangible book ratio option to uncover these additional values. In this case, the value of the assets should be reduced by the size of any secured loans tied to them. If it’s obvious that a company is trading for less than its book value, you have to ask yourself why other investors haven’t noticed and pushed the price back to book value or even higher. The P/B ratio is an easy calculation, and it’s published in the stock summaries on any major stock research website.
The book value per share of a company is the total value of the company’s net assets divided by the number of shares that are outstanding. The book value of equity (BVE) is the value of a company’s assets, as if all its assets were hypothetically liquidated to pay off its liabilities. Value investors look for relatively low book values (using metrics like P/B ratio or BVPS) but otherwise strong fundamentals in their quest to find undervalued companies.
Clear differences between the book value and market value of equity can occur, which happens more often than not for the vast majority of companies. With those three assumptions, we can calculate the book value of equity as $1.6bn. Investors use BVPS to gauge whether a stock is trading below or above its intrinsic value.

Xin chào! Tôi là Luna Nguyễn người làm nội dung trên website: tracuudisc.com . Mọi góp ý của các bạn đều là động lực giúp chúng tôi hoàn thiện hơn vậy nên đừng ngại ngùng hãy comment suy nghĩ của các bạn khi trải nghiệm trên website tracuudisc.com nhé!
